
Frequency modulation block diagram Download Scientific Diagram
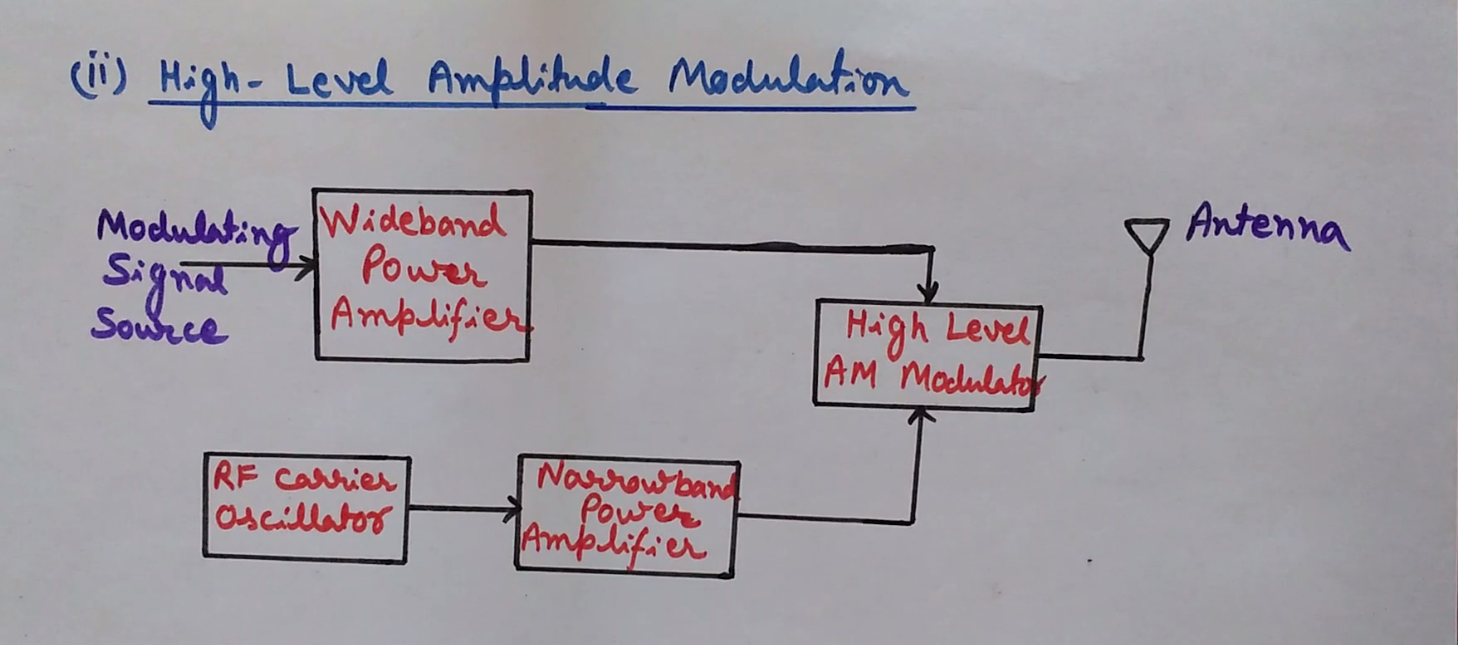
Block Diagram of Modulation Types Of Modulation Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Mathematical Representation Frequency Spectrum AM Transmitter Oscillator Power Amplifier Class A Power Amplifier Class B Power Amplifier Class C Power Amplifier Low-Level AM Transmitter High-Level AM Transmitter Advantages of AM Disadvantages of AM

Frequency modulation block diagram Download Scientific Diagram
Definition, Block diagram for Delta Modulation and Demodulation, applications of Delta modulation - Electronics Coach Delta Modulation (DM) Definition: A modulation technique that converts or encodes message signal into a binary bit stream is known as Delta Modulation.
Principal Of Communication Notes (Amplitude Modulation Definition, Types, )
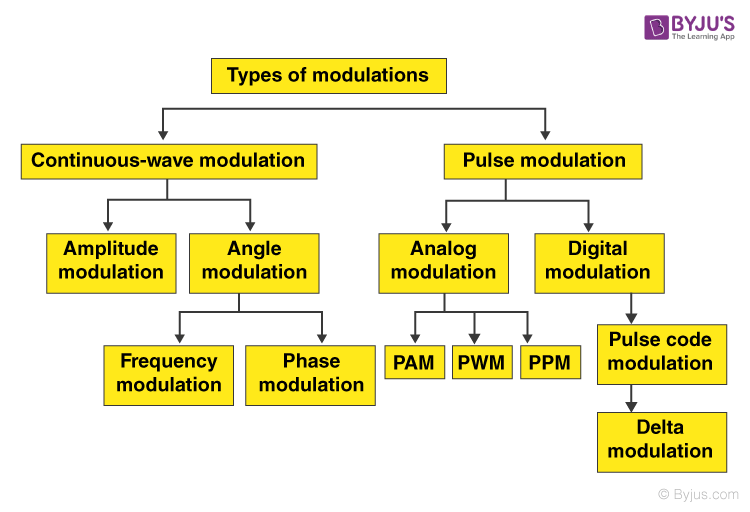
A block diagram showing the basic classification of modulation techniques is given below: Also, Read: Amplitude Modulation Frequency Modulation Types of Pulse Modulation Lets us look at some of the different types of pulse modulation. Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) It is the simplest form of pulse modulation.
Pulse Modulation Definition, Types, Block Diagrams, Pulse Modulation Width
Delta-sigma (ΔΣ; or sigma-delta, ΣΔ) modulation is an oversampling method for encoding signals into low bit depth digital signals at a very high sample-frequency as part of the process of delta-sigma analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs). Delta-sigma modulation achieves high quality by utilizing a negative feedback loop during quantization to the lower.
27 High Level Block Diagram Wiring Diagram List
Block diagram of Pulse Code Modulation The figure below shows the block diagram representing a PCM system It is basically composed of a transmitter, a transmission path and a receiver. The transmitter performs the sampling, quantizing and encoding of the signal.

Download Frequency Modulation Png Gantt Chart Excel Template
Figure 2: A simple block diagram of delta modulation technique Applications of the Delta Modulation technique Generally, the Delta Modulation method is used where the signal quality has low importance, as it is the simplest version of DPCM, and it does not have a significant accuracy, especially when signal changes are too high or near zero.

PPM Pulse Position Modulation Block diagram, Waveforms, Advantages, Disadvantages
The process by which data/information is converted into electrical/digital signals for transferring that signal over a medium is called modulation. It increases strength for maximum reach of the signals. The process of extracting information/data from the transmitted signal is called demodulation.
Phaselocked Loop Modulation Block Diagram Signal, PNG, 1049x1024px, Phaselocked Loop, Area
Fig.3 GMSK Modulation Block Diagram As shown in the GMSK modulator Gaussian filter is applied to NRZ signal after it is passed through integrator block. This gives Φ. By applying COS and SIN function to this Φ gives out I and Q components which bits with cos and sin function respectively using mixing function. Both the chains are summed up.
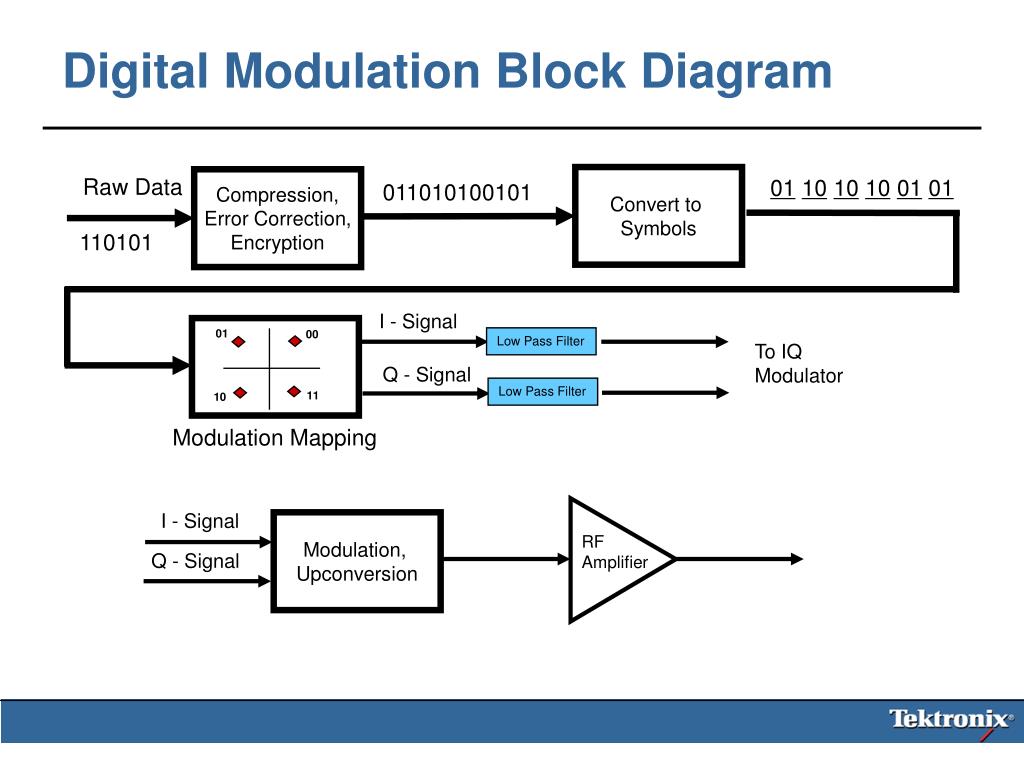
PPT WCA102 Fundamentals of Digital Modulation PowerPoint Presentation ID410205
Block Diagram. Delta modulation uses the over-sampling technique to achieve high signal-to-noise ratio. In delta modulation system, the transmitter circuit is composed of a Summer, Quantizer, Accumulator and an Encoder interconnected with each other. Delta-Modulation-and-Demodulation. Here, the integrator circuit contains a delay of Ts.

Pulse Code Modulation(PCM) Block Diagram, Working Principle ETechnoG
QAM can be defined as it is s a modulation technique that is used to combine two amplitude modulated waves into a single channel to increase the channel bandwidth. Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Block Diagram The below diagrams show the transmitter and receiver block diagram of the QAM scheme. QAM Modulator qam-modulator QAM Demodulator

Block diagram of FSO communication systems using PPMMSKSIM. (a)... Download Scientific Diagram
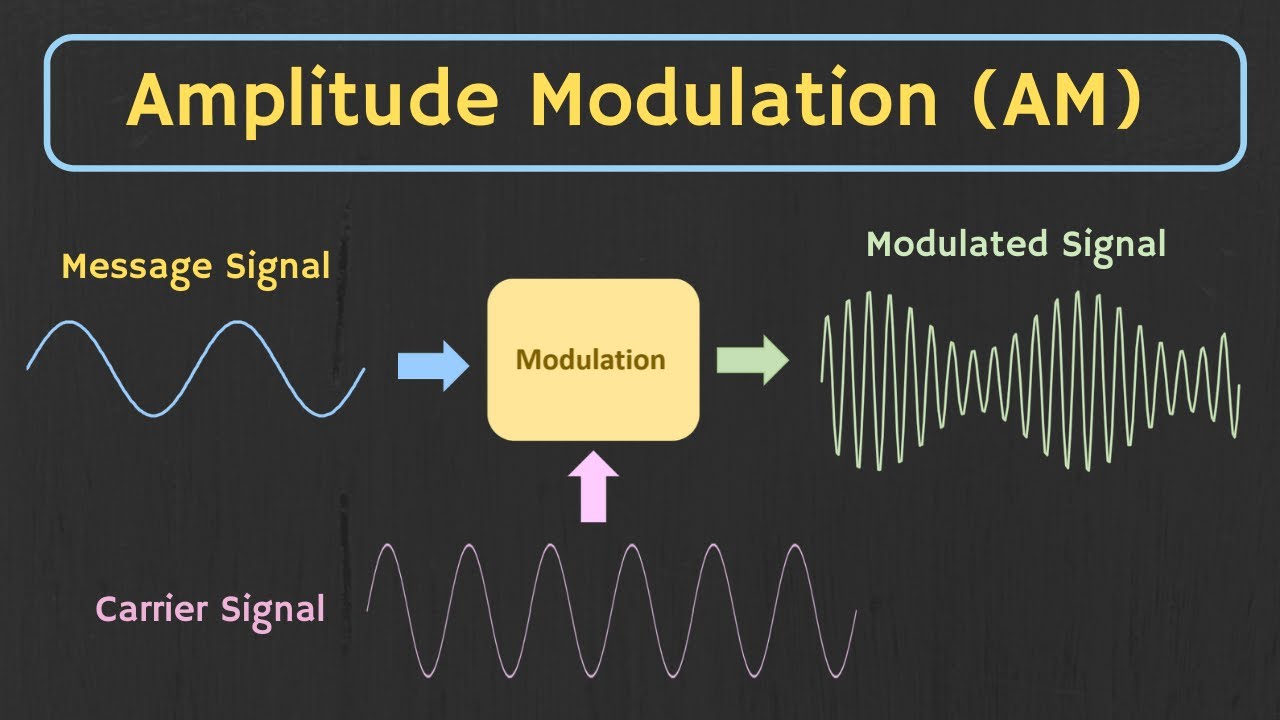
Amplitude Modulation Block Diagram Here the modulating signals might be an audio or video signal. These are also called as baseband signals as these are modulated with the carrier signals. Carriers are extremely high-frequency radio signals, In general, carrier signals are received from the RF oscillators.
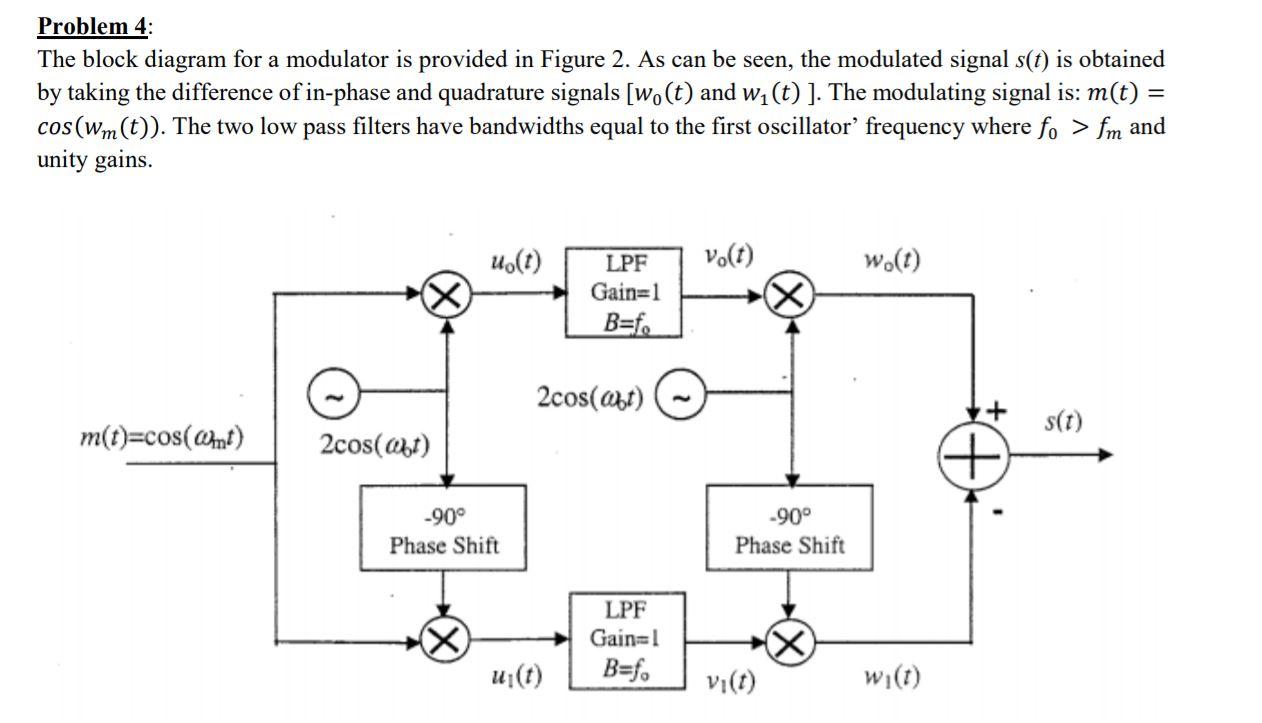
Solved Problem 4 The block diagram for a modulator is
Delta Modulation is a simplified form of DPCM technique, also viewed as 1-bit DPCM scheme. As the sampling interval is reduced, the signal correlation will be higher. Delta Modulator. The Delta Modulator comprises of a 1-bit quantizer and a delay circuit along with two summer circuits. Following is the block diagram of a delta modulator.

Differential modulation block diagram for (a) QPSK, and (b) 16 QAM (τ... Download Scientific
Amplitude Modulation Block Diagram. Generation of Amplitude Modulation : There are two types of devices in which it may be necessary to the Generation of Amplitude Modulation. The first of these, the AM transmitter, generates such high powers that its prime requirement is efficiency, so quite complex means of AM generation may be used.

Simplified schematic diagram of the pulse width modulator block. Download Scientific Diagram
Fig. 1 shows block diagram of the modulation where the signal is modulated by the carrier signal. There are the three key parameters of the modulation, which is amplitude, phase, and frequency.
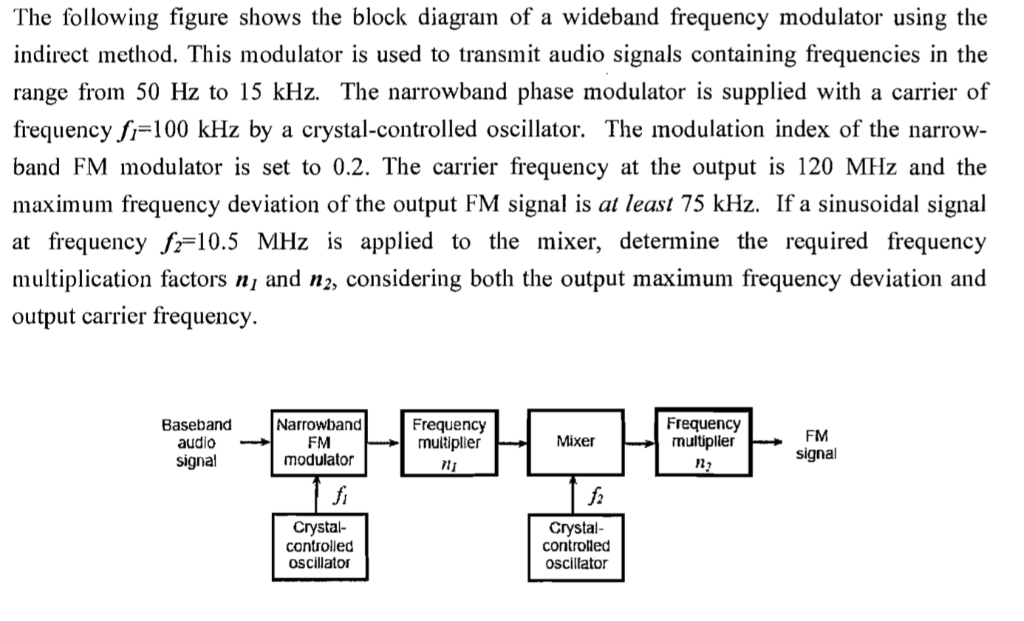
The following figure shows the block diagram of a
Block Diagram of Delta Modulator The sampling rate is comparatively very high in the delta modulation technique. The value of the step size after quantization is smaller. In the delta modulation process, the quantization design is easy and simple, and it gives the user the option to design the bit rate.

5 Block Diagram of QAM Modulation Transmitter Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 2.13.4: Quadrature modulator block diagram. In PSK modulation i(t) and q(t) have the same amplitude and indicate a phase ϕ of the modulated carrier so that i(t) = cos[ϕ(t)] and q(t) = sin[ϕ(t)]. The particular example shows two possible values of Ik and Qk and this indicates QPSK modulation. the modulated signal.